Muslims and Buddhists have come together to demand full autonomy and regular statehood from New Delhi. They have been resolving their religious differences and working together, setting a great template for the rest of India.
India’s Ladakh Is a Unique Case of Religious Coexistence
Shining BD Desk || Shining BD
Muslims and Buddhists have come together to demand full autonomy and regular statehood from New Delhi. They have been resolving their religious differences and working together, setting a great template for the rest of India.
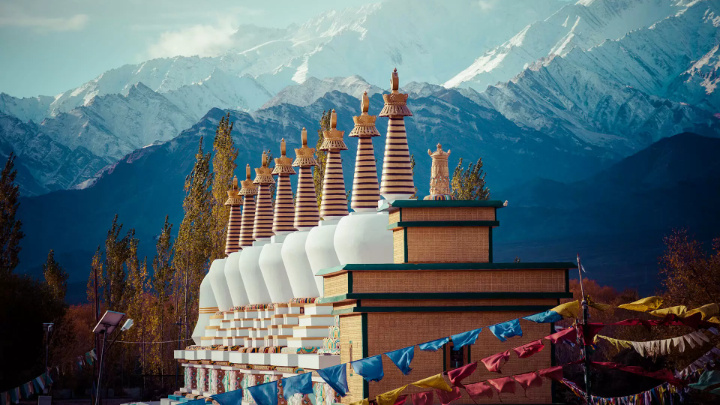
Until 2019, Ladakh was a part of the Jammu and Kashmir state. Since then, it has become a union territory with Buddhism and Islam are its main two religions.
Buddhism first came to Ladakh in the first century of the common era during the reign of the Kushan Empire. For centuries, Buddhism flourished practically unchallenged by other religions. In the 15th century, however, the spread of Islam in Ladakh began through the migration of Muslim traders from Kashmir, Afghanistan, and Central Asia. They started coming to Ladakh, settling there, and marrying local Buddhist women.
Today, Muslims comprise 46.6% of Ladakh’s population while Buddhists form 39.7%. Yet the Ladakhi tradition of peaceful coexistence continues. Even as anti-Muslim sentiment has been rising in India, Ladakh remains a model of religious tolerance.
Buddhist Dominate and New Delhi-Run
For centuries, Tibet has been influencing the culture and religious practices in Ladakh and Tibetan refugees have been finding refuge in the region. The first large wave of Tibetans arrived in India in 1959 following the Chinese invasion of Tibet. Now, there are more than 6,500 Tibetans living in Ladakh. The cultural heritage of Ladakhis and Tibetans is similar, which is why Ladakh is often called “Little Tibet.”
The Dalai Lama emphasized the common Buddhist heritage of Ladakhis and Tibetans in a recent visit. Yet few realize that Muslims are the majority community in Ladakh and have been an integral part of its region’s social, cultural, and religious landscape for thousands of years.
As per India’s opposition-run paper National Herald, Ladakh’s administration showcases Buddhist culture and ignores Muslim culture. Many make the argument that Ladakh has little autonomy. Ladakhis lack a “legislature and [are] without powers over laws affecting livelihoods and community rights.”
What Lies Behind India’s Bold Bet on Kashmir?
As a union territory, Ladakh is ruled by the central government in New Delhi. Indian states elect their chief ministers and legislatures have considerable power. This is not the case with union territories. They have elected members too but these legislators have much less power than their counterparts in the state.
Recently, Professor Sheikh Showkat from the Central University of Kashmir observed: “Ladakhis thought once they will get the union territory status, they will be the masters of their own land. But that has proved to be a nightmare for them because a union territory has very little power and most of the decision-making happens in New Delhi.”
Muslim-Buddhist Relations Still Cordial
The removal of special status for Jammu and Kashmir in 2019 led to Ladakh emerging as a separate territory. At first, this deepened the Muslim-Buddhist divide. Following the decision, people in Kargil took to the streets to protest. Those in Leh, on the other hand, celebrated the move.
The mood quickly changed, however, as Leh’s residents became worried about their job security and job prospects. Consequently, they have been opposing the new political order. This has been bringing the two main religious communities closer. Both Muslims and Buddhists have been unitedly demanding more political representation, statehood, and self-governance. \
Ladakh has its own culture, traditions, and language, making it distinctive in India. While prejudices based on religious differences exist, Muslims and Buddhists of Ladakh have social, ethnic, and linguistic similarities. Hence, they have a shared sense of Ladakhi identity. Yet this identity has been under threat. Most young Ladakhis are migrating out of the region. The need to protect this identity might be one reason why any inter-religion disagreements are typically resolved quickly. The situation in Ladakh is significantly less tense than in many other parts of India such as the country’s largest state of Uttar Pradesh where Muslims regularly fall victim to religious discrimination and violence. Certain inter-religious disagreements will always persist but it seems that Ladakh has found a way to approach them in a way that allows this territory to preserve peace and harmony.
Source - Katarzyna Rybarczyk, The Fair Observer
Shining BD